KV Botnet
Original Issue Date:-
April 12, 2024
Virus Type:- Botnet
Severity:-
Medium
It has been reported that a botnet dubbed “KV Botnet”, is targeting Small Office/Home Office (SOHO) routers and VPN devices. The botnet can be utilized for various malicious activities, including data exfiltration, espionage, and network disruption.
Infection Mechanism
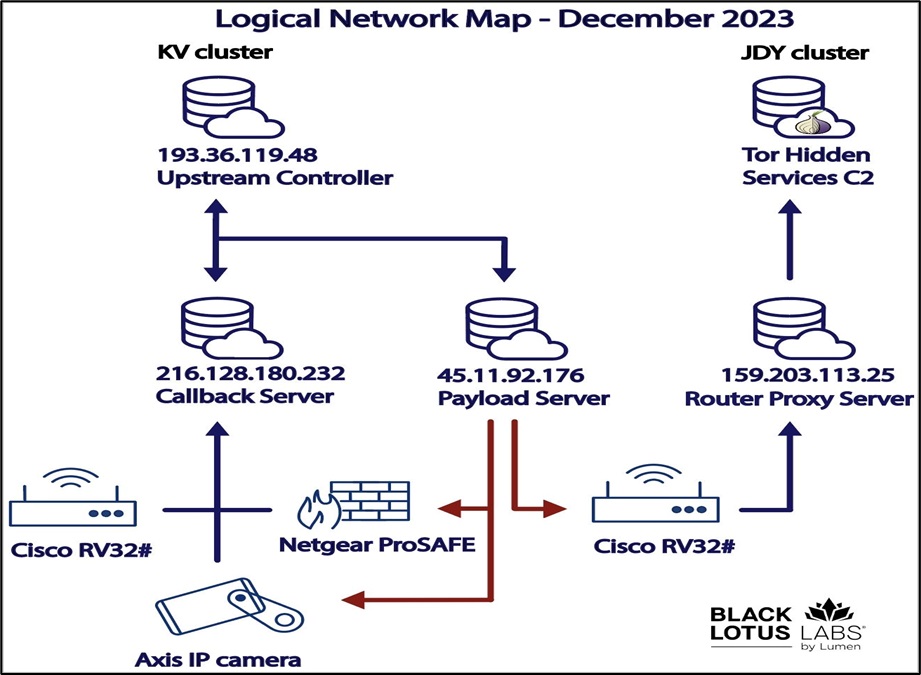
The KV Botnet is a hidden network that transfers data secretly. It is created by hacking small office/home office routers and firewalls from popular brands such as Fortinet, NETGEAR and Cisco etc. This botnet is operated by two separate sections: one section infects devices, and the other section transmits data. This botnet is believed to be associated with a Chinese state-sponsored hacking group known as Volt Typhoon, also referred to as Bronze Silhouette.
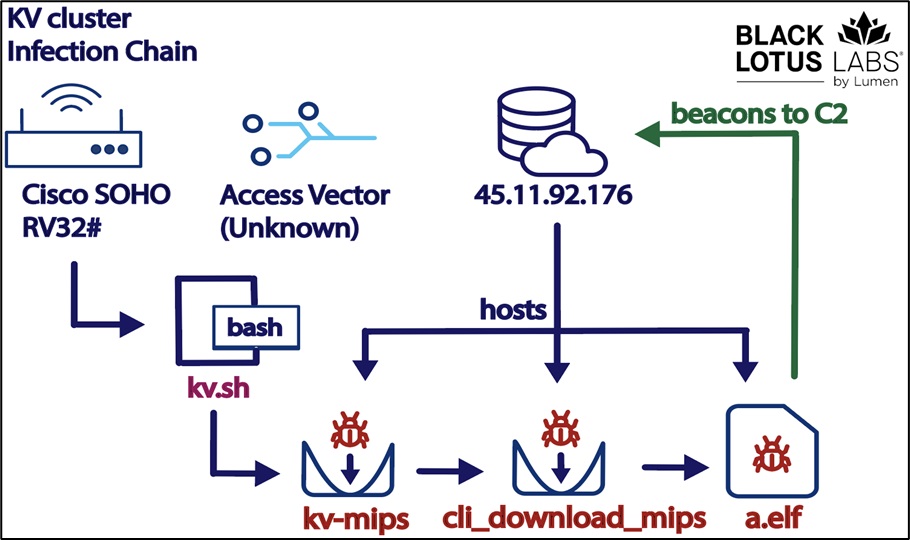
The KV botnet is designed to exploit vulnerabilities in firmware and web interfaces of small office/home office (SOHO) devices. It uses brute-force attacks to crack weak passwords for admin accounts and gain access to the devices. The botnet can also infect devices through third-party applications or malicious firmware updates.
Once infected, the malware creates a hidden communication channel within the device and uses it for:
- Data exfiltration: Stealing sensitive data, including user credentials, financial information, and confidential documents, from the infected network.
- Lateral movement: The malware is spreading through the network, attempting to compromise more devices.
- Command and control: Attackers can take control of systems, using them to launch DDoS attacks or deploy malware.
Indicator of Compromise:
IP:- 207.246.100[dot]151
- 66.42.124[dot]155
- 104.156.246[dot]150
- c524e118b1e263fccac6e94365b3a0b148a53ea96df21c8377ccd8ec3d6a0874
- 2711f1341d2f150a0c3e2d596939805d66ba7c6403346513d1fc826324f63c87
- 5928f67db54220510f6863c0edc0343fdb68f7c7070496a3f49f99b3b545daf9
- Kv-all.sh (Cisco)- 7043ffd9ce3fe48c9fb948ae958a2e9966d29afe380d6b61d5efb826b70334f5
- Kv-arm - 690638c702170dba9e43b0096944c4e7540b827218afbfaebc902143cda4f2a7
- Kv-mipsel - 48299c2c568ce5f0d4f801b4aee0a6109b68613d2948ce4948334bbd7adc49eb
For more detailed list of IoC, kindly refer the below URL:
Best Practices and Recommendations:
- Implement all accounts with complex password logins (e.g., service accounts, admin accounts, and domain admin accounts) to have strong, unique passwords.
- Implement multi-factor authentication for all services to the extent possible, particularly for webmail, virtual private networks, and accounts that access critical systems.
- Remove unnecessary access to administrative shares.
- Network segmentation and segregation into security zones - help protect sensitive information and critical services. Separate administrative network from business processes with physical controls and Virtual Local Area Networks.
- Do not browse un-trusted websites or follow un-trusted links and exercise caution while clicking on the link provided in any unsolicited emails and SMSs.
- Monitor system/ VM resources activity for any abnormal high usage.
- Use a host-based firewall to only allow connections to administrative shares via server message block (SMB) from a limited set of administrator machines.
- Enable protected files in the Windows Operating System to prevent unauthorized changes to critical files.
- Disable remote Desktop Connections, and employ least-privileged accounts. Limit users who can log in using Remote Desktop, and set an account lockout policy. Ensure proper RDP logging and configuration.
- Keep the operating system, and third-party applications (MS Office, browsers, browser Plugins) up-to-date with the latest patches.
- Restrict access using firewalls and allow only to selected remote endpoints, VPN may also be used with a dedicated pool for RDP access.
- Additional Security measures that may be considered are::
- Use RDP Gateways for better management
- Change the listening port for the Remote Desktop
- Tunnel Remote Desktop connections through IPSec or SSH
- Two-factor authentication may also be considered for highly critical systems
References:


