CLOP Ransomware
Original Issue Date:- July 23, 2020
Virus Type:- Ransomware
Severity:- High
It is reported that the ransomware named “CLOP” is active in attacking organizations/institutions across the globe. Post compromise this ransomware leaks information if negotiation deal of ransom fails. Recently the threat actors behind Clop have stolen and encrypted the sensitive information of various organizations and after failure of ransom payment, the stolen information was leaked on their 'CL0P^_- LEAKS' data leak site, hosted on dark web. The leaked information includes data backups, financial records, thousands of emails and vouchers etc.
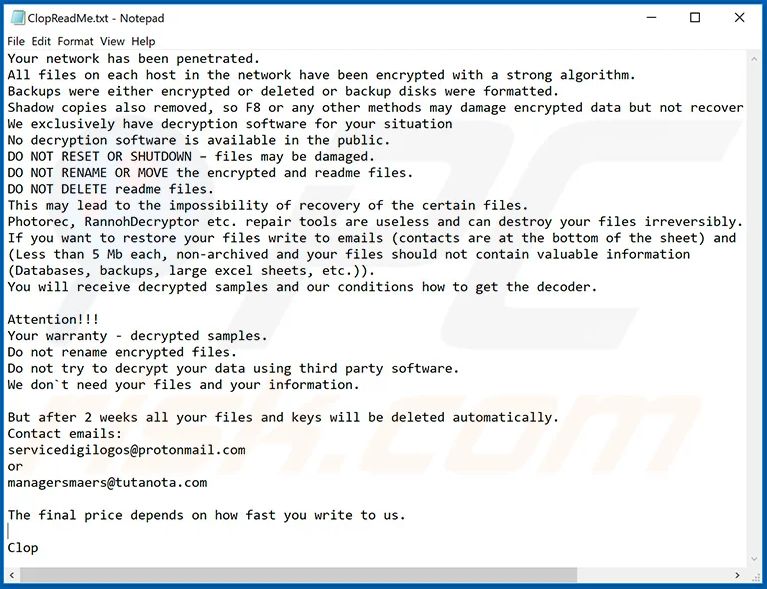
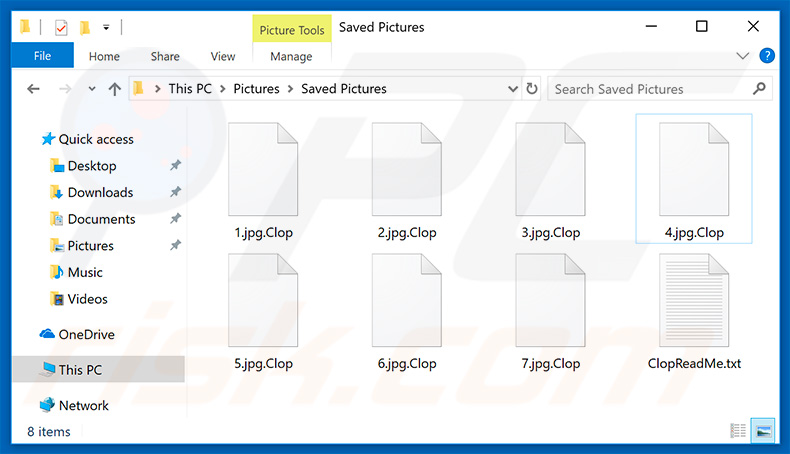
After encryption CLOP ransomware appends “.Clop” extension in each file and generates a text file "ClopReadMe.txt" containing ransom note in each folder. CLOP ransomware uses RSA (Rivest-Shamir-Adleman) encryption algorithm and generated keys are stored on a remote server controlled by Clop operators.
Updated versions of Clop have tried to expand their attack vectors through disabling and removing local security solutions such as Windows Defender and Microsoft Security Essentials etc. This ransomware has capability of installing additional password stealing Trojans and other malware infections.
In most cases, Clop is distributed via fake software updates, trojans, cracks, unofficial software download sources, and spam emails. In the recent attack on an Indian conglomerate, it is suspected that the bug (CVE-2019-19781) in the Citrix Netscaler ADC VPN gateway was utilized to carry out the attack. Unfortunately, as of now no decryptor tool is available for Clop ransomware.
Indicators of compromise:
Hashes:
- 6d115ae4c32d01a073185df95d3441d51065340ead1eada0efda6975214d1920
- 6d8d5aac7ffda33caa1addcdc0d4e801de40cb437cf45cface5350710cde2a74
- 70f42cc9fca43dc1fdfa584b37ecbc81761fb996cb358b6f569d734fa8cce4e3
- a5f82f3ad0800bfb9d00a90770c852fb34c82ecb80627be2d950e198d0ad6e8b
- 85b71784734705f6119cdb59b1122ce721895662a6d98bb01e82de7a4f37a188 (unpacked)
- 2ceeedd2f389c6118b4e0a02a535ebb142d81d35f38cab9a3099b915b5c274cb
- 00e815ade8f3ad89a7726da8edd168df13f96ccb6c3daaf995aa9428bfb9ecf1
- 0d19f60423cb2128555e831dc340152f9588c99f3e47d64f0bb4206a6213d579
- 408af0af7419f67d396f754f01d4757ea89355ad19f71942f8d44c0d5515eec8
- 7e91ff12d3f26982473c38a3ae99bfaf0b2966e85046ebed09709b6af797ef66
- a867deb1578088d066941c40e598e4523ab5fd6c3327d3afb951073bee59fb02
Emails:
- servicedigilogos@protonmail[d0t]com
- managersmaers@tutanota[d0t]com
- unlock@eqaltech[d0t]su
- unlock@royalmail[d0t]su
- unlock@goldenbay[d0t]su
- unlock@graylegion[d0t]su
- kensgilbomet@protonmail[d0t]com
Files Detection/aliases:
- Ransom.Win32.CLOP.D
- Ransom.Win32.CLOP.D
- Ransom.Win32.CLOP.F
- Ransom.Win32.CLOP.F.note
- Ransom.Win32.CLOP.M
- Ransom.Win32.CLOP.THBAAAI
- Trojan.BAT.CLOP.A
- Trojan.BAT.CLOP.A.component
- Trojan.Win32.CLOP.A.note
For detailed IOC (Hashes, Files etc), please refer the links provide in references.
Countermeasures and Best practices for prevention:
- Do not download and install applications from untrusted sources [offered via unknown websites/ links on unscrupulous messages]. Install applications downloaded from reputed application market only.
- Update software and operating systems with the latest patches. Outdated applications and operating systems are the targets of most attacks.
- Don't open attachments in unsolicited e-mails, even if they come from people in your contact list, and never click on a URL contained in an unsolicited e-mail, even if the link seems benign. In cases of genuine URLs close out the e-mail and go to the organization’s website directly through browser.
- Install ad blockers to combat exploit kits such as Fallout that are distributed via malicious advertising.
- Prohibit external FTP connections and blacklist downloads of known offensive security tools.
- All operating systems and applications should be kept updated on a regular basis. Virtual patching can be considered for protecting legacy systems and networks. This measure hinders cybercriminals from gaining easy access to any system through vulnerabilities in outdated applications and software. Avoid applying updates / patches available in any unofficial channel.
- Restrict execution of Power shell /WSCRIPT in an enterprise environment. Ensure installation and use of the latest version of PowerShell, with enhanced logging enabled. Script block logging and transcription enabled. Send the associated logs to a centralized log repository for monitoring and analysis.
https://www.fireeye.com/blog/threat-research/2016/02/greater_visibilityt.html - Establish a Sender Policy Framework (SPF) for your domain, which is an email validation system designed to prevent spam by detecting email spoofing by which most of the ransomware samples successfully reaches the corporate email boxes.
- Application whitelisting/Strict implementation of Software Restriction Policies (SRP) to block binaries running from %APPDATA% and %TEMP% paths. Ransomware sample drops and executes generally from these locations.
- Users are advised to disable their RDP if not in use, if required, it should be placed behind the firewall and users are to bind with proper policies while using the RDP.
- Block the attachments of file types, exe|pif|tmp|url|vb|vbe|scr|reg|cer|pst|cmd|com|bat|dll|dat|hlp|hta|js|wsf
- Consider encrypting the confidential data as the ransomware generally targets common file types.
- Perform regular backups of all critical information to limit the impact of data or system loss and to help expedite the recovery process. Ideally, this data should be kept on a separate device, and backups should be stored offline.
- Network segmentation and segregation into security zones - help protect sensitive information and critical services. Separate administrative network from business processes with physical controls and Virtual Local Area Networks.
References:
- https://success.trendmicro.com/solution/000151740-CLOP-Ransomware-Information
- https://www.pcrisk.com/removal-guides/14451-clop-ransomware
- https://www.mcafee.com/blogs/other-blogs/mcafee-labs/clop-ransomware/
- https://cyware.com/news/clop-ransomware-shows-its-presence-again-targets-indian-conglomerate-fbecf72a
- https://github.com/albertzsigovits/malware-notes/blob/master/Ransomware/Clop.md


